What is Micrognathia?
|
Time to read 5 min
|
Time to read 5 min
Micrognathia is when the jawbone is smaller than normal. In some cases, this can cause problems with feeding, breathing, and sleeping. This occurs in about 1 in every 1,500 births.
In certain cases, when the jaw's size is small enough, it can hinder the baby's eating. Infants who suffer from this issue could require nipples that are specially designed for proper feeding.
Micrognathia could cause the teeth to be not appropriately aligned. It is evident by the way that the teeth are closed. There is often not enough room to grow.
Children suffering from this condition must see an orthodontic specialist when the adult teeth begin to appear since children can overcome the issue, it is often logical to hold off treatment until a child is older.
Micrognathia is generally congenital. This means that the children are born with the condition. Certain cases of micrognathia may be caused by genetic disorders, and in others, it's caused by genetic mutations that develop independently and aren't able to transfer through family members.
Here are some genetic disorders that can be associated with micrognathia:
Pierre Robin syndrome
Pierre Robin syndrome causes your baby's jaw to grow gradually in the womb, which results in a tiny lower jaw. This also causes your baby's tongue and teeth to recede into the throat. This may block the airways and cause breathing difficulties.
They could be born with an opening on the mouth's roof (or the cleft palate). It is seen in one in every 8,500 to 14,000 births.
Trisomy 13 and 18
A trisomy is a genetic disorder that develops in babies who have an extra gene: three chromosomes rather than the usual two. The trisomy can lead to extreme mental and physical defects.
As per the National Library of Medicine, around 1 out of 16,000 newborns is affected by trisomy 13, commonly referred to as Patau syndrome.
As per the Trisomy 18 Foundation, around 1 out of 6,000 infants suffer from Trisomy 18.
A number such as 13 or 18 refers to the chromosome the extra material comes from.
Achondrogenesis
Achondrogenesis is a rare, inherited disorder that occurs when your children's pituitary gland does not produce enough growth hormone. This can lead to severe bone disorders that include a narrow lower jaw and an enlarged chest. This also leads to extremely short:
Progeria
Progeria Genetic disorder is a genetic condition that causes your child's age increases quickly. Progeria-afflicted babies typically do not display signs at birth; however, they begin to show indications of the disorder in the first two years of life.
This is due to a genetic change; however, it's not passed on via families. Along with a narrow jaw, people who suffer from progeria might also experience slow growth, hair loss, and the appearance of a narrower face.
Cri-du-chat syndrome
Cri-du-chat Syndrome is an uncommon genetic disorder that causes developmental impairments and physical malformations, like small jaws and lower-set ears.
Treacher Collins syndrome
Treacher-Collins syndrome is a genetic condition that can cause severe facial anomalies. Along with a smaller jaw, it could result in a mouth that is cleft and cheekbones that are not present, as well as a defect in the shape of ears.
The symptoms of micrognathia may vary between children; however, they may also be characterized as:
Discover More: How Do Teeth Get Demineralized?
The diagnosis of micrognathia is often made during pregnancy based on the ultrasound signs. Also, it can be detected upon delivery based on the way the jaw of your child looks.
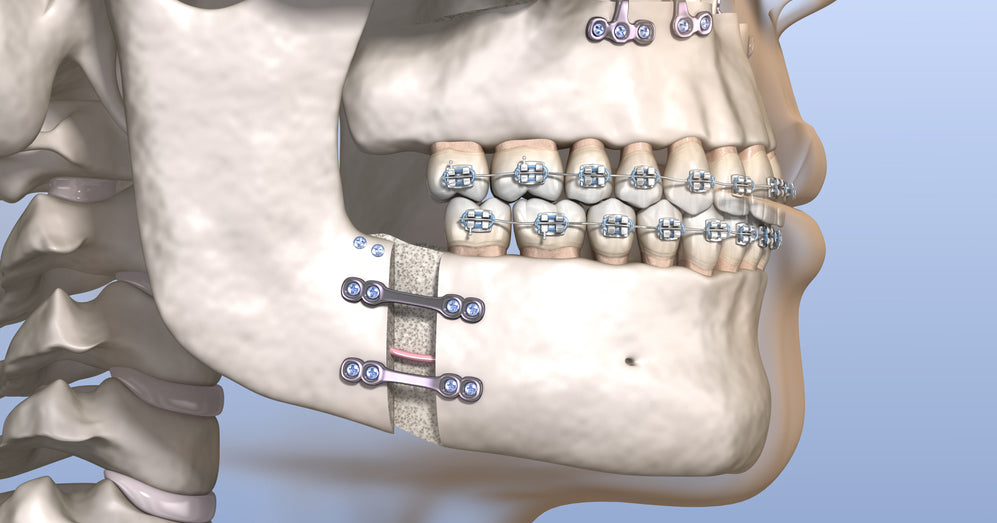
In certain cases, micrognathia can improve on its own. There are both surgical and nonsurgical solutions for micrognathia. Which one is best for your child is contingent on the degree of severity of the issue.
Nonsurgical Treatment For Micrognathia
Surgical Treatment For Micrognathia
Effective bad breath remedies include:
Gentle and regular scraping of the tongue
Regular oral care practices such as daily brushing and flossing
Professional deep cleanings and plaque removal
The ongoing use of oral probiotics.
One, the probiotics compete with the existing bad bacteria and reduce their presence by “crowding them out”
Two, the probiotics produce BLIS or “bacteriocin-like-inhibitory-substances” which is a technical way of stating that one probiotic strain (bacteria) can produce a substance that inhibits or kills off other bacteria. Three, by working to control gingivitis, gum disease and tooth decay these probiotics reduce the very sources of bacteria-generated odors in the mouth.
Studies have shown a clear reduction in plaque levels and gingivitis symptoms when oral probiotics were administered to patients with moderate to severe gingivitis.


